Everyone’s been saying it (and, frankly, we tend to agree): We are currently in unprecedented times. It may feel like a cliche. But truly, when you stop and look around right now, not since the advent of the first consumer-friendly smartphone in 2008 has the digital web design and development industry seen such vast technological advances.
A few of these innovations have been kicking around for decades, but they’ve only moved into the greater public consciousness in the past year. Versions of artificial intelligence (AI) and chatbots have been around since the 1960s and even virtual reality (VR)/augmented reality (AR) has been attempted with some success since the 1990s (That Starner). But now, these technologies have reached a tipping point as companies join the rush to create new products that leverage AI and VR/AR.
What should we do with all this change? Let’s think about the immediate future for a moment (not the long-range future, because who knows what that holds). We at Oomph have been thinking about how we can start to use this new technology now — for ourselves and for our clients. Which ideas that seemed far-fetched only a year ago are now possible?
For this article, we’ll take a closer look at VR/AR, two digital technologies that either layer on top of or fully replace our real world.
VR/AR and the Vision Pro
Apple’s much-anticipated launch into the headset game shipped in early February 2024. With it came much hype, most centered around the price tag and limited ecosystem (for now). But after all the dust has settled, what has this flagship device told us about the future?
Meta, Oculus, Sony, and others have been in this space since 2017, but the Apple device has debuted a better experience in many respects. For one, Apple nailed the 3D visuals, using many cameras and low latency to reproduce a digital version of the real world around the wearer— in real time. All of this tells us that VR headsets are moving beyond gaming applications and becoming more mainstream for specific types of interactions and experiences, like virtually visiting the Eiffel Tower or watching the upcoming Summer Olympics.
What Is VR/AR Not Good At?
Comfort
Apple’s version of the device is large, uncomfortable, and too heavy to wear for long. And its competitors are not much better. The device will increasingly become smaller and more powerful, but for now, wearing one as an infinite virtual monitor for the entire workday is impossible.
Space
VR generally needs space for the wearer to move around. The Vision Pro is very good at overlaying virtual items into the physical world around the wearer, but for an application that requires the wearer to be fully immersed in a virtual world, it is a poor experience to pantomime moving through a confined space. Immersion is best when the movements required to interact are small or when the wearer has adequate space to participate.
Haptics
“Haptic” feedback is the sense that physical objects provide. Think about turning a doorknob: You feel the surface, the warmth or coolness of the material, how the object can be rotated (as opposed to pulled like a lever), and the resistance from the springs.
Phones provide small amounts of haptic feedback in the form of vibrations and sounds. Haptics are on the horizon for many VR platforms but have yet to be built into headset systems. For now, haptics are provided by add-on products like this haptic gaming chair.
What Is VR/AR Good For?
Even without haptics and free spatial range, immersion and presence in VR is very effective. It turns out that the brain only requires sight and sound to create a believable sense of immersion. Have you tried a virtual roller coaster? If so, you know it doesn’t take much to feel a sense of presence in a virtual environment.
Live Events
VR and AR’s most promising applications are with live in-person and televised events. In addition to a flat “screen” of the event, AR-generated spatial representations of the event and ways to interact with the event are expanding. A prototype video with Formula 1 racing is a great example of how this application can increase engagement with these events.
Imagine if your next virtual conference were available in VR and AR. How much more immersed would you feel?
Museum and Cultural Institution Experiences
Similar to live events, AR can enhance museum experiences greatly. With AR, viewers can look at an object in its real space — for example, a sarcophagus would actually appear in a tomb — and access additional information about that object, like the time and place it was created and the artist.
Museums are already experimenting with experiences that leverage your phone’s camera or VR headsets. Some have experimented with virtually showing artwork by the same artist that other museums own to display a wider range of work within an exhibition.
With the expansion of personal VR equipment like the Vision Pro, the next obvious step is to bring the museum to your living room, much like the National Gallery in London bringing its collection into public spaces (see bullet point #5).
Try Before You Buy (TBYB)
Using a version of AR with your phone to preview furniture in your home is not new. But what other experiences can benefit from an immersive “try before you buy” experience?
- Test-drive a new car with VR, or experience driving a real car on a real track in a mixed-reality game. As haptic feedback becomes more prevalent, the experience of test-driving will become even closer to the real thing.
- Even small purchases have been using VR and AR successfully to trial their products, including AR for fashion retail, eyeglass virtual try-ons, and preview apps for cosmetics. Even do-it-yourself retailer Lowe’s experimented with fully haptic VR in 2018. But those are all big-name retailers. The real future for VR/AR-powered TBYB experiences will allow smaller companies to jump into the space, like Shopify enabled for its merchants.
- Visit destinations before traveling. With VR, you could visit fragile ecosystems without affecting the physical environment or get a sense of the physical space before traveling to a new spot. Visitors who require special assistance could preview the amenities beforehand. Games have been developed for generic experiences like deep sea diving, but we expect more specific travel destinations to provide VR experiences of their own, like California’s Redwood Forest.
What’s Possible With VR/AR?
The above examples of what VR/AR is good at are just a few ways the technology is already in use — each of which can be a jumping-off point for leveraging VR/AR for your own business.
But what are some new frontiers that have yet to be fully explored? What else is possible?
- What if a digital sculptor or 3D model maker could create new three-dimensional models in a three-dimensional virtual space? The application for architects and urban planners is just as impactful.
- What if medical training could be immersive, anatomically accurate, and reduce the need for cadavers? What if rare conditions could be simulated to increase exposure and aid in accurate diagnoses?
- What if mental health disorders could be treated with the aid of immersive virtual environments? Exposure therapy can aid in treating and dealing with anxiety, depression, and PTSD.
- What if highly skilled workers could have technical mentors virtually assist and verify the quality of a build? Aerospace, automotive, and other manufacturing industry experts could visit multiple locations virtually and go where they’re needed most.
- What if complex mathematic-based sciences could provide immersive, data-manipulative environments for exploration? Think of the possibilities for fields like geology, astronomy, and climate change.
- What if movies were told from a more personal point of view? What if the movie viewer felt more like a participant? How could someone’s range of experiences expand with such immersive storytelling?
Continue the AR/VR Conversation
The Vision Pro hasn’t taken the world by storm, as Apple likely hoped. It may still be too early for the market to figure out what AR/VR is good for. But we think it won’t go away completely, either. With big investments like Apple’s, it is reasonable to assume the next version will find a stronger foothold in the market.
Here at Oomph, we’ll keep pondering and researching impactful ways that tomorrow’s technology can help solve today’s problems. We hope these ideas have inspired some of your own explorations, and if so, we’d love to hear more about them.
Drop us a line and let’s chat about how VR/AR could engage your audience.
Portable Document Format, or PDF, files have been around since 1992, offering a software-agnostic solution for presenting and sharing digital documents. For organizations that existed before the ’90s, PDFs became an easy way to move from physical to digital; they could take the same documents they used to print and now share them digitally as PDFs.
A few years after PDFs were officially launched, CSS came onto the scene as the preferred computer language for styling web pages. Over the following three decades, PDF capabilities grew alongside CSS and other digital technologies, giving creators new ways to lay out and publish their content.
Fast forward to today. Developers worldwide (Oomph among them) have been making websites for a while. We have online forms, interactive databases, and of course, plain old text on a webpage. And yet, PDFs persist.
What’s So Bad About PDFs?
Mobile Phones
Think of the last time you tried looking at a PDF on your phone. First off, there’s the issue of finding it. Depending on your operating system and browser, the file might open right in a new browser tab, or it might download and disappear into some folder you forgot about until this exact moment. (And of course, when you find the folder, you realize this is the fifth time you’ve downloaded this same file.)
Now that you’ve opened the file, you see the tiny text of an 8.5” x 11” page shrunk to a quarter of its intended size. So you pinch, zoom, and drag the page around your screen. You might rotate your phone to the dreaded horizontal orientation to fit a whole line of text at once. If this PDF is a fillable form, you may be simply out of luck on your mobile device unless you’re ready to go down a rabbit hole of separate apps and workarounds.
If, for just a minute, we want to ignore the massive amount of mobile usage — including the 15% of American adults who fully depend on phones for internet access — there’s plenty more cause for PDF concern.
Accessibility
Let’s talk about accessibility. There’s a good chance that your digital properties, including PDFs, are legally required to conform to accessibility standards. This is true for government entities — both federal and more recently, state, local, and district governments, thanks to a Title II update — as well as businesses and nonprofit organizations.
Beyond the legalities, the CDC reports that about 27% of American adults have a disability. While not all 70 million of these people use a screen reader, we know some people use assistive technology even if they don’t identify as having a disability. (When’s the last time you pressed a button to open a door just because your hands were full or to let a large group of people pass through?) Improvements for the sake of accessibility, more often than not, lead to a more effortless, more intuitive experience for everyone.
While it’s possible to make a PDF accessible, the process for doing so is extensive and involves several manual checks. This can be so time-consuming and specialized that businesses and professionals dedicate themselves entirely to remediating PDFs for accessibility.
Of course, making a website accessible isn’t as easy as plug-and-play, but accessibility should already be built into the system. Content editors who are not technical professionals can publish accessible content with relative ease on an accessible website platform (as long as we can all remember not to link “click here”) but are typically left to their own devices when it comes to documents.
Brand Reputation
Beyond these critical issues, there are a few more problems that are less vital to users but could have a negative business impact.
For one, documents like PDFs open up a whole world of styling possibilities. The flexibility might feel like a benefit at first, but give it a little time and I’m certain you’ll start seeing inconsistencies from one document to the next. Add in a few more people preparing these files, and those small differences will pile up, giving users an impression that maybe the business is not quite as put together as they thought. (Not to mention that every change in presentation is asking users to understand a new format, slowing them down or confusing them.) Consistency is key to building a trustworthy brand; every unnecessary variation erodes that trust.
There’s also the near certainty that the information provided in PDFs will need updating. When that happens, you’d better make sure to delete the old file in favor of the new one and update all your links. Since the file format made it easy (or necessary) for users to download the content to their devices, there’s a greater chance that they’ll hold onto old information, even though a newer version is now on the website.
Finally, storing important information in PDFs gives you less control over optimizing for search engines. Google has a tough time reading PDF content (though proper tagging and metadata will help), so these files often rank lower in search results than webpages with similar content. The more that content lives in PDFs and not webpages, the more your SEO will suffer, and the less likely people will be to find and consume your content.
What You Can Do Instead
Like I said, PDFs solved a real problem… 30 years ago. They still have their place today, but more often than not, there’s a better way.
Does It Need To Be a PDF?
When the PDF is just a basic document of text, we recommend turning that into a basic webpage of text. It’s easy to say, but making it happen might mean taking a fresh look at why that information is in a PDF in the first place.
Custom Layout
If you’re using PDFs to create a certain layout, consider how you can achieve something similar through CSS. You might be able to build something you like using the layout and style options already available in your CMS, but you probably won’t create a perfect 1:1 match.
Any design in a Word or Google document can also exist on a webpage. If there’s a certain design you use time and time again in your PDFs that you just can’t recreate with the web editing tools, you might need some new code. It becomes an exercise in prioritization to weigh the benefits of building a custom layout against the time and cost of doing so.
Also, remember that a design that works well for a printed page may not be the best design for a responsive webpage. Rather than recreating the exact layout digitally, ask yourself what you’re trying to achieve with the layout and whether there’s a better way to meet that same goal. While unique designs may be more difficult to create on a webpage than a PDF, I’d urge you to consider this a benefit in most cases. Limitations create consistency, which will most likely simplify the experience for both content editors and users.
Designing for Print
Speaking of print, that might be another reason for including PDFs. You may know that a portion of your audience will want to print out the page, maybe to annotate it or to have it on hand as they complete a related task.
In reality, you can serve this user without sacrificing everyone else’s online experience. Developers can use targeted CSS to customize how a webpage will print or export — including what content will display and its styling. Going this route affects how the page will print with the browser tool, and you could even provide a “Print” link if that’s a common need. Ultimately, targeted CSS means the printed content can look as similar or different from the webpage as needed.
Process
Another common cause for PDFs is that they’re simply baked into the content publishing process. Whether from fear of changing approved content or a lack of knowledge around what’s possible in the CMS, content teams may use PDF uploads as a fallback for publishing the information quickly and moving on.
A solution here may be to bring your site editor into the process sooner. As the web expert, they can speak to what will work well and what might need to change when moving the content to a webpage. The site editor may need to be heavily involved at first, but their load should lighten as the writers and other team members learn the website’s needs.
In some cases, it might also be worth building new CMS templates, such as content types. This can be especially helpful for reinforcing consistency when several people manage the website. If the content needs to follow a specific format, a highly structured edit form can act as an outline. You can share this template with the original content creators so that everyone is working toward a shared goal.
Repurposed Content
Most likely, your organization does more than manage a website. Maybe you have a brick-and-mortar office with brochures and paperwork, or you host webinars with branded slide decks. There are plenty of reasons you might create and share documents other than uploading them onto your website, but you still want the same information available online. And since it’s already put together, the easiest way to share it could be to upload the PDF.
Unfortunately, this is a situation where easy doesn’t cut it. The same tri-fold brochure that looks professional and appealing on a reception desk can be confusing and annoying on a computer or phone. A printed form works great for in-office visitors, but a web form can give users the benefits of autocomplete and progressive disclosure they’ve come to expect online.
The best experience for your users requires attention to their context. Ultimately, we need to be intentional and thoughtful about what users need in their current situation, which may require different presentations of the same content.
Embrace Digital
We’re not expecting to see the end of PDFs on websites anytime soon. For one, sometimes it’s simply out of your control. Maybe you’re providing an official government form that only exists as a fillable PDF. Even if the document is internally produced, change may be lengthy and involved, requiring buy-in from those who hold the purse strings.
While we wait for the world to change, we can advocate for a better user experience. If a PDF “needs” to stay, maybe you can duplicate the most important content onto the page linking to it. If you have any control over the document itself, you can test for accessibility and make sure it’s properly tagged. Get started with the tools and guidance we’ve collected in this accessibility resources document.
How easily your audience can access your information and services sets the tone for how they perceive your organization. The good news is that there’s so much you can do to make their experience positive, no matter how they choose to interact with your content. If you need help, let us know.
A world without third-party cookies is fast approaching. Big-name browsers like Safari and Firefox already block them by default, and Google Chrome — the biggest browser of them all — is set to follow.
First, a quick refresher: Websites use cookies to store data in your browser specific to that website and other sites. The question, though, is who the website is storing the data for. Third-party cookies store data that allows advertising services to track your behavior on any given site, while first-party cookies are those a website uses for its own purposes.
Like most things, not all cookies are created equal. As browsers transition to these new defaults, some will make the grade, while others will be blocked for good. What does this mean for your website, and how can you get ahead of the change? We’ll walk you through it.
Are Cookies Really Going Away?
That depends on the type of cookies your site uses. Browsers are slowly blocking third-party cookies by default — those associated with cross-site tracking for ad networks like Facebook or LinkedIn — but first-site, or same-site, cookies will remain.
That means that if retargeting is essential to your paid marketing strategy, you may need to rethink your approach. But any cookies you use to support your site features and functionality can keep on keeping on, assuming your users have agreed to the use of those cookies on your site. For example, you may be able to keep track of previously viewed content and use that information to suggest other relevant content to that user. So don’t say goodbye to your cookie consent services either; you still have to give users the chance to opt out of any first-party cookies.
Why Now? Haven’t We Been Using Cookies Forever?
While cookies have been a web-surfing staple for almost as long as we’ve been using the internet, that’s not necessarily a good thing.
Legislation like GDPR in Europe, the California Consumer Privacy Act, and the New York Privacy Act are tightening restrictions on the use of consumer data, and rapidly increasing cybersecurity threats in recent years have illuminated the risks of large-scale data storage. Consumers have also begun to prize their privacy, realizing that their information is valuable and no organization should be looking over their shoulder as they browse.
Ultimately, phasing out third-party cookies is about doing what’s best for your users. Making the move now can help instill trust in your website, since users know you aren’t capturing their data behind the scenes. Cookie consent forms also put the data you do use out in the open, showing users that your organization takes their privacy seriously and is prepared to protect it.
How Will The End of Third-Party Cookies Impact My Industry?
Not all organizations will feel the shift equally. We’ve seen some verticals get ahead of the curve, while others are naturally less reliant on third-party cookies. Here are some key industry-specific areas to consider.
Healthcare
Strict privacy laws and regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) have turned healthcare organizations into pioneers in this area. The Office of Civil Rights even published a bulletin warning organizations about third-party cookies.
Many of the healthcare brands we support at Oomph are already focused on safeguarding user privacy because they’re used to doing it with medical records. One of our clients, for example, is already exploring adopting an in-house analytics tool hosted on their own server. If your healthcare organization is relying on third-party cookies for any marketing efforts, analytic insights, or other website features, start thinking now about the best way to phase them out.
Higher Education
Many institutions we work with are using third-party cookies because of digital efforts to drive student enrollment. When implementing personalization cookies, be sure they are implemented with the proper “SameSite” attribute value. Then be sure to engage your vendors; we’ve encouraged many of our higher education clients to explore how their vendors are preparing for this transition.
Nonprofits
Like higher education, nonprofits should review the vendors and larger ad networks they rely on to build their volunteer base or drive donations. Many nonprofits don’t use these services, but those that do should get ahead of the change, otherwise you may stand to lose an important fundraising channel.
4 Steps To Prepare for the End of Third-Party Cookies
Cookies, analytics, and cross-site tracking might all sound like areas best left to the pros. But there’s a lot you can do to prepare your organization for the move away from cookies, as well as critical opportunities to pull in a vendor to maintain the functionality you need.
Audit Your Site
A website audit should always be your first step. Taking stock of the cookies you use is the best way to get a handle on the changes you’ll need to make. Tapping your web partner is a great idea here, too. Your vendor should be able to identify existing third-party cookie warnings, which can help shape your audit.
For example, while we were updating a client’s email marketing integration recently, Chrome notified our developer that our client’s vendor was sending third-party cookies. We then reached out to the vendor to continue the conversation, knowing that those cookies had to be addressed.
Identify Affected Cookies
The goal of your audit is to identify all third-party cookies that won’t make the cut. Don’t stop by just listing the cookie, either. Review what function it serves and the role it plays in your organization’s digital footprint. You may have to get rid of the cookie, but that doesn’t mean you have to ditch the strategy it’s tied to.
Reach Out to Your Vendors
Ask vendors about their plans to handle the transition away from third-party cookies, and feel out whether they’ll still be able to offer the service they currently provide. Consider it a red flag if the vendor is uninformed or unprepared; you might have to seek out alternatives if there’s even the slightest chance your current vendor will be defunct by the end of the year.
Design Alternatives
The end of third-party cookies is daunting, but it’s also exciting. Take this opportunity to innovate on your users’ behalf. How can you design engaging new experiences that still exceed their expectations? That’s more than possible, so long as you have the right tools in place.
This could be a self-hosted analytics tool you build yourself or new local storage solutions to replace the role of cookies. You might also consider a fully authenticated experience for the users of your site. Lean on a trusted partner here, too. Vendors with website expertise can guide you toward the right solution for you and your users.
Cookies on the Brain?
For many organizations, this is the most they’ve thought about cookies in years. Third-party cookies have become so essential to building a business online, and yet they’ve largely flown under our radar. But while this change may feel overwhelming, making the switch doesn’t have to be.
Here at Oomph, we see this as a golden opportunity for organizations to put their users first, and we’re already taking steps to help our clients do just that.
Need a hand bringing your website into a world beyond third-party cookies? Let’s talk about it.
THE BRIEF
A Creative Beacon Sets a New Path
The RISD Museum is the 20th largest art museum in the United States with over 100,000 objects in its collection, including Ancient art, costumes, textiles, painting, sculpture, contemporary art, furniture, photography, and more. The museum occupies more than 72,000 square feet in three historic and two contemporary buildings along Providence’s bustling South Main Street and riverfront.
We often say that a website redesign is more like a collective therapy session — it’s an opportunity to air grievances in a safe space, to think about the future untethered to the present situation, and make decisions that could change the course of the organization. Since many websites are more than just a marketing platform, a redesign can affect the entire organization and the way they communicate their value to their own team and the world.
At the heart of this project were large, existential questions:
What does it mean to be a physical institution collecting physical objects in a digital world?
What do viewers want out of a museum experience in an interactive space?
Can a museum be more relaxed about how viewers will interpret the work?

Open Source the Museum’s Entire Collection
Behind the Museum’s initiative to re-platform the website from a closed system to an open source system like Drupal 8 was another, perhaps even larger, initiative: a plan to “open source” the museum’s entire collection. They will bring all 100,000 objects online (they have a little over 13,000 available prior to launch, a mere 13%) and use a Creative Commons license system that allows visitors to download and repurpose high-resolution images whenever the objects are in the public domain. This was the heart of the revolution upon which the RISD Museum was about to embark.
THE APPROACH
MuseumPlus & Drupal 8 equals Open Access
The heavy lift for our engineers was an integration with RISD’s museum software, MuseumPlus. MuseumPlus needed to continue to be the source of truth for any object, artist, or exhibition. The teams again collaborated extensively to work towards an API that could provide all the correct information
between the two databases, and a system of daily jobs and manual overrides to start a synchronization process. As the online connection grows, these connections will be the critical link between the public-facing object data and the internal records.
The aesthetics of the site became a structural backdrop for the objects, artwork, and images of people in the physical spaces of the museum.
Gray and white wireframes evolved into a black and white interface that kept information clear and clean while allowing the colors of the artwork to shine through. Language around the site’s architecture was simplified and tested for clarity. An element of time — words like Soon, Upcoming, Now, Ongoing, Past — keeps the visitor grounded around the idea of a physical visit, while open access to objects online serves a whole community of art lovers and historians that may never be able to visit in person.
A bold storytelling idea came out of our collective collaborative process — the homepage experience opens with four videos, a cinematic exterior shot and three interior videos that explore the three main sections of the navigation. The homepage becomes a gateway into the physical space. Choosing a path via the navigation takes the viewer inside to explore the spaces and the objects. Instead of a homepage that assumes a visitor wants to see everything and then choose something to explore deeper, this one introduces them to the content in a way that connects them to the physical space.

THE RESULTS
An Evolving Partnership
Site visit patterns have seen significant improvement — sessions per user and pages per session have increased while bounce rate has decreased. Thanks are due in part to the new hosting environment with Acquia, which has provided hefty speed increases and stability — page load times have decreased, server response time is significantly less, and page download time is far less as well.
As the RISD Museum grows their online collection even further, we have identified a backlog of ideas that we’d love to address, from a more fully featured search, an integrated audio guide, and a more open and collaborative way for users to share back what they have done with the museum’s assets. A new Drupal 8 (now 10) implementation gives the museum plenty of room to grow virtually. The collaborative relationship between Oomph and the RISD Museum is only beginning.
High-quality content management systems (CMS) and digital experience platforms (DXP) are the backbone of modern websites, helping you deliver powerful, personalized user experiences. The catch? You have to pick your platform first.
At Oomph, we have a lot of love for open-source platforms like Drupal and WordPress. Over the years, we’ve also built applications for our clients using headless CMS tools, like Contentful and CosmicJS. The marketplace for these solutions continues to grow exponentially, including major players like Adobe Experience Manager, Sitecore, and Optimizely.
With so many options, developers and non-developers with a project on the horizon typically start by asking themselves, “Which CMS or DXP is the best fit for my website or application?” While that is no doubt an excellent question to consider, I think it’s equally important to ask, “Who is going to implement the solution?”
CMS/DXP Solutions Are More Alike Than You Might Think
I recently attended the annual Healthcare Internet Conference and spoke with quite a few healthcare marketers about their CMS tools. I noticed a common thread: Many people think their CMS (some of which I mentioned above) is hard to use and doesn’t serve them well.
That may very well be the case. Not all CMS tools are created equal; some are better suited for specific applications. However, most modern CMS and DXP tools have many of the same features in common, they just come at different price points. So here’s the multi-million dollar question: If most of these products provide access to the same or similar tools, why are so many customers displeased with them?
Common Challenges of CMS/DXP Implementation
Often, we find that CMS users get frustrated because the tool they chose wasn’t configured to meet their specific needs. That doesn’t necessarily mean that it was set up incorrectly. That’s the beauty of many of today’s CMS and DXP products: They don’t take a one-size-fits-all approach. Instead, they allow for flexibility and customization to ensure that each customer gets the most out of the product.
While enticing, that flexibility also burdens the user with ensuring that their system is implemented effectively for their specific use case. In our experience, implementation is the make-or-break of a website development project. These are just a handful of things that can derail the process:
- The implementation partner didn’t fully understand how their client works and configure features accordingly.
- The demands of user experience overshadowed the needs of content editors and admins.
- Hefty licensing fees ate away at the budget, leaving behind funds that don’t quite cover a thorough implementation.
- The project was rushed to meet a tight deadline.
- The CMS introduces new features over time that add complexity to the admin or editing experience.
- Old features get sunsetted as new capabilities take their place.
Most of the work we do at Oomph is to help our clients implement new websites and applications using content management systems like Drupal. We have decades of combined experience helping our clients create the ideal user experience for their target audience while also crafting a thoughtful content editing and admin experience that is easy to use.
But what does that look like in practice?
4 Steps for a Successful CMS Implementation
Implementation can be the black box of setting up your CMS: You don’t know what you don’t know. So, we like to get our clients into a demo environment as soon as possible to help them better understand what they need from their CMS. Here’s how we use it to navigate successful CMS implementation:
- Assess the Capabilities of the CMS
The first step can be the most simple at face value. Consider what the CMS needs to do for you, then find a CMS that includes all of those features. Content modeling (more on that below) is a key part of that process, but so is auditing your team’s abilities.
Some teams may be developer-savvy and can handle less templated content-authoring features. Others may need a much more drag-and-drop experience. Either use case is normal and acceptable, but what matters is that you identify your needs and find both a CMS and an implementation process that meets them. That leads us to the next point.
- Test-Drive the CMS Early and Often
You wouldn’t buy a car without test-driving it first. Yet we find that people are often more than willing to license a CMS without looking under the hood.
Stepping into the CMS for a test drive is a huge part of getting the content editing experience right. We’ve been designing and engineering websites and platforms using CMS tools for well over a decade, and we’ve learned a thing or two along the way about good content management and editing experiences.
Even with out-of-the-box, vanilla Drupal, the sky’s the limit for how you can configure it. But that also means that nothing is configured, and it can be difficult to get a sense of how best to configure and use it. Rather than diving into the deep end, we work with our clients to test the waters. We immediately set up a project sandbox that offers pre-configured content types, allowing you to enter content and play with a suite of components within the sleek drag-and-drop interface.
- Align User Experience with Content Authoring
Beyond pre-configured content and components, our sandbox sites include a stylish, default theme. The idea is to give you a taste both of what your live site could look like and what your content authoring experience might be. Since so many teams struggle to balance those two priorities, this can be a helpful way to figure out how your CMS can give you both.
- Finalize Your Features & Capabilities
While a demo gives you a good idea of the features you’ll need, it might include features you don’t. But discovering where our pre-built options aren’t a good fit is a good thing — it helps us understand exactly what YOUR TEAM does and does not need.
Our goal is to give you something tangible to react to, whether that’s love at first type or a chance to uncover capabilities that would serve you better. We’ve found this interactive yet structured process is the CMS silver bullet that leads to a better outcome.
Content Modeling
Another key part of our project workflow is what we call content modeling. During this phase, we work with you to identify the many content types you’ll have on your website or application. Then, we can visualize them in a mapping system to determine things like:
- What relationships exist between these different content types?
- Who should have access to a content type, and what governance should be in place to ensure all content is accurate, on brand, and approved for publishing?
- What features do you need to support content at every level? For example, at the field level, do you need a drop-down with predefined values that only certain people can edit, or do you need an open-text field a content editor can customize?
With a solid content model in place, we can have a higher level of confidence that our CMS implementation will create the right content editing experience for your team. From there, we actually implement the content model in the CMS as soon as possible so that you can test it out and we can make refinements before getting too far along in the process.
Content Moderation & Governance
Many clients tell us they either have too much or too little control over their content. In some cases, their content management system is so templated or rigid that marketing teams can’t quickly spin up landing pages and instead have to rely on development teams to assist. Other teams have too much freedom, allowing employees to easily deploy content that hasn’t been approved by the appropriate team members or strays from company brand standards.
Here at Oomph, our mantra is balance. A good content editing process needs both flexibility and governance, so teams can create content when they need to, but avoid publishing content that doesn’t meet company standards. Through discovery, we work with clients to determine which content types need flexibility and which ones don’t.
If a content type needs to be flexible, we create a framework that allows for agility while still ensuring that users can only select approved colors, font types, and font sizes. We also identify which content needs to be held in moderation and approved before it can be published on the website.
Taking the time to discuss governance in advance creates a CMS experience that strikes the right balance between marketing freedom and brand adherence.
Implementation Turns a Good CMS Into a Great One
Modern CMS/DXP solutions have mind-blowing features, and they will only continue to get more complex over time. But the reality is that while picking a CMS that has the features you need is important, how it’s configured and implemented might matter even more. After all, how helpful is it to have a CMS with embedded artificial intelligence if making simple copy updates to your home page is a nightmare?
Implementation is the “it” factor that makes the difference between a CMS you love and one you’d rather do your job without.
Interested in solving your CMS headaches with better implementation? Let’s talk.
Have you ever waved to someone and they didn’t wave back? Awkward, right? But are you sure they could see you and recognize you? Was the sun in their eyes? Were you too far away? Were you wearing a face mask?
There is a similar situation with your branding on your website. On a smaller mobile device, is your logo legible, or are the words shrunk down and too small? Are the colors high-contrast enough to be seen on a sunny day? Is there consistency between your social media avatar and your website, between your print materials and your digital advertising? Can customers recognize your brand wherever it might be displayed?
For your brand to be the most successful, it takes a little extra effort to think through all of these possible scenarios. But it’s worth it, or your customers will give you the cold shoulder, whether they intended to or not.
This extra bit of strategy and planning around your brand is called “Responsive Branding.” Just like responsive design, where your website’s content adapts to the device a customer is using, responsive branding adapts to the device, the medium, and the platform while also considering situations like low light, high light, animated, or static.
Oomph works with organizations across industries to build or refresh responsive brands that serve and delight their users across the full spectrum of digital experiences. Here’s what we’ve learned about responsive branding and our tips for creating one that works.
What Is Responsive Branding?
Let’s first start with what you’ve probably already heard — responsive web design. Coined by Ethan Marcotte in 2010, the “responsive” part came to mean that a web design responded to the size of the screen, from a phone to a tablet to a widescreen desktop monitor.
Then came responsive logos. These take the elements of the main logo and adapt them for different sizes and use cases. A logo might have too much detail to be legible as a small social media icon, for example.

Responsive Branding blends these ideas and looks at the design system holistically. A successful responsive brand may include:
- A logo version for different sizes and applications. Variations might include one with the tagline, one without, one with a mark and typeface, one just the name, one just the mark, the possibilities go on!
- Secondary logo options which may include abbreviations, monograms, or different combinations of the main elements
- When applicable, an internationalized version of the wordmark and tagline
- A color palette that can provide variation while addressing accessibility and situations of low light or high glare
- A fluid typography system that provides contrast between sizes within different size media (including print!)
- A fluid spacing system
- Motion when appropriate, like video intros and outtros
Why Responsive Branding Matters
Your business makes a huge investment in building a brand that stands apart from the competition while communicating your personality and value. You are building trust with customers through every interaction. When your brand works well in one situation but not another, it erodes trust.
A strong brand will be clear, understandable, and memorable for all users in all situations. Whether you have physical locations or digital ones, the brand works with the same consistent strength and message every time.
When you invest in a responsive brand, you:
- Make your brand more visible. More users can connect with you when you have a brand that’s both recognizable and responsive. Given that 60% of consumers are more likely to buy from a brand they recognize, the opportunity cost of not getting this right is huge.
- Improve accessibility. Digital accessibility means people of all abilities can use your website and experience your brand. Up to 1 in 4 American adults live with a disability, so a lack of accessibility means fewer customers to reach. For visual brand elements, that means considerations for color blindness, low vision, and cognitive impairments like dyslexia.
- Create a more consistent brand. Responsive branding equips your team with the tools to express your brand effectively across mediums. That means less time involved in building new assets and a more consistent experience that meets your users’ high expectations.
3 Elements of a Responsive Brand
A responsive brand is more than a shape-shifting logo. The most responsive brands make strategic use of these three elements:
1. Logo

Your logo is the first piece of your brand that customers will recognize. Using a single-state logo can compromise that impression — a logo that looks great at a large scale is often unintelligible as a small icon.
Responsive logo designs help ensure your logomark is clear and impactful no matter where you apply it. Beyond the size considerations we mentioned, it should include different formats like horizontal, vertical, and square to support many different digital, social, and print platforms.
Some other techniques we use to create scalable logos include:
- Dropping words or lettering
- Dropping the icon or image
- Creating an abbreviation version
- Stacking the icon/image and text/lettering
- Combining separate elements into a single icon
- Simplifying details and shapes within logo marks
- Varying thickness and white space to make small logos more legible
Oomph Tip: It’s okay to take several design rounds to get it right. Iterating helps uncover where you’ll use the logo, what it must convey, and which colors and iconography can best support that purpose. We went through several design iterations with our client AskRI before settling on a bold, simple font and clear chat bubble icon that plays off the state of Rhode Island’s distinctive shape.
Color Palette

A responsive color palette is less about picking complementary shades on a color wheel and more about creating an experience that works in all situations. People with visual impairments and people on low-lit smartphones, for example, rely on high-contrast color combinations to engage with your brand.
Start by following the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), which include specific recommendations for color contrast ratios. Colors that meet that standard include light text with dark backgrounds, or vice versa.
Depending on where your brand appears, you may need to adjust your color palette for different settings. For example, your full-color logo might look stunning against a solid white background but becomes illegible against bright or dark colors. A single color logo is useful for some digital use cases like Windows web icons and iOS Pinned Tabs. In non-digital spaces, single color logos are great when color printing isn’t an option, such as with engraving or embroidery. Build out alternate color variations where necessary to make sure your palette works with you – not against you – across your materials.
Oomph Tip: If your brand palette is already set in stone, try playing with the brightness or saturation of the values to meet recommendations. Often your brand colors have a little wiggle room when combinations are already close to passing corformance ratios. Check out our article about this issue for more pointers.
Typography and Layouts

Responsiveness is also important to consider when structuring web pages or marketing collateral. The most legible layouts will incorporate adaptable typography with clear contrast and simple scaling.
When selecting a font, be sure to think about:
- Minimum legible sizes. When is small too small? It depends, of course, but don’t forget older customers, those with low vision, or those in situations that make reading more difficult. Use at least a 16px size for digital products and 12pt size for print. These might change depending on the font, but these sizes are a great place to start.
- Inclusive typefaces. Many designers overlook how understandable certain letterforms appear to be. A way to quickly review is to look at the number 1, lowercase l (L), and uppercase I (i) of any typeface. Then also look at the capital O, the zero, and the lowercase o — 1lI O0o. Can you tell the difference when these characters are out of context? If you can’t, then your customers might have trouble as well. Use your judgment, but also use this trick to expose possible problems with your communication. These five keys to accessible web typography are a great place to start.
- Scaling ratios. Similar to a musical scale of harmonious notes, a typographic scale is a collection of font sizes that work well together. Using a typographic scale helps to make your text visually appealing and readable for different users across different devices. Some examples include exponential scales, where you multiply the previous font size by a ratio to get the next font size, and Fibonacci sequences, where you add a number from the Fibonacci set to the base font value to get a new size in the scale.
Oomph Tip: Don’t go it alone. Tools like Typescale and Material UI’s The Type System can simplify typography selection by recommending font sets that meet usability and scalability requirements. And the U.S. Design System has some suggestions as to which typefaces are the most accessible.
How To Get Started With Responsive Branding
To create a responsive brand that resonates, you first have to identify what elements you need and why you need them. That second part is your secret sauce: finding a balance between a design your users can recognize and one that inspires them.
A design audit can zero in on the needs of your brand and your audience, so you can create a responsive design system that meets both. Not sure where to start? Let’s talk.
Change is the only constant in life, and the same goes for accessibility. Our understanding of how to create truly accessible websites is always evolving, and so are the standards for measuring if we’ve succeeded.
The most recent update to the Website Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) — released on October 5, 2023 — is the latest attempt to help brands make their digital experiences more accessible for all users.
Don’t panic, WCAG 2.2 isn’t an overhaul. But it does shift the previous standards, delivering more specific and, in some cases, more realistic guidelines that make compliance easier (good news, website managers!). While WCAG 2.2 isn’t cause for alarm, it is something to get out in front of. Here’s what to know about WCAG, the ins and outs of the latest updates, and what it all means for your website.
What Is WCAG, Anyway?
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines set the standard for accessible website design. WCAG first issued design guidance in 1999, but the 2008 WCAG 2.0 laid the groundwork for accessibility today. Those standards created a framework for designing websites that are perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust for people of varying abilities.
2018’s WCAG 2.1 wasn’t a radical departure from its predecessor, but it did add criteria related to mobile devices and users with vision and cognitive impairments. By 2023, accessibility had become widely understood and embraced as essential for inclusive design. That shift helped usher in WCAG 2.2, an update based on multiple years of research and review.
WCAG 2.2 adds nine new success criteria split across three different levels, A, AA, and AAA:
- Level A: This is the WCAG minimum, and it now includes two additional success criteria.
- Level AA: Websites that achieve AA status go beyond the basics. We advise our clients to achieve Level AA as much as possible, depending on their audience.
- Level AAA: Websites that implement all WCAG guidelines to the highest degree can achieve AAA status. We recommend our clients do so when it suits their website and their users’ needs. For example, a healthcare organization serving older patients may need the highest level of color contrast on its site, while a university serving young students may not.
The WCAG 2.2 update didn’t just add criteria; it made some criteria obsolete, others weaker, and still others more essential than ever. Specifically, WCAG 2.2 promoted 2.4.7 Focus Visible from Level AA to Level A, which means all websites will need visual indicators that show which page feature is in focus. It also changed the recommended size of touch targets, making it easier for designers everywhere to comply.
What WCAG Standard Am I Required to Meet?
The standard you’re required to meet depends on your industry:
- State and Local Governments: Organizations in the public sector have the most explicit accessibility requirements. The Department of Justice (DOJ) recently announced a proposed rule that requires state and local governments to meet WCAG 2.1 Level AA standards for their websites and mobile apps.
- Private Sector: Accessibility in the private sector is less regulated, but complying with WCAG guidelines is in your best interest. One reason is that noncompliance could open your company up to a lawsuit. A recent report estimated that 4,220 ADA website lawsuits would be filed by the end of 2023 — almost double the number filed in 2018.
Though there is no official standard in courts, the DOJ has referenced WCAG 2.1 Level AA in past filings. We expect the courts to slowly start referencing 2.2 as cases catch up, but it might take another year for version 2.2 to become the standard.
While wanting to stay out of court is understandable, legal requirements are only one reason to adopt WCAG. Millions of users around the world use screen readers and other assistive devices. Those users have buying power and they want to engage with your organization, whether that’s registering to vote, signing up for a class, or making an appointment with their healthcare provider. When your website is accessible, you’re able to connect with the broadest audience possible — likely earning more loyal users in the process.
WCAG 2.2 Checklist
While achieving inclusive website design is an exciting prospect, the nuts and bolts of getting there can feel anything but. Here, we help you visualize what the new guidelines mean in practice. You might be surprised by how accessible your website already is.
Guideline 2.4: Navigable
The standards under guideline 2.4 address anything that will make it easier for users to move through your website.
2.4.11 Focus Not Obscured (Minimum) (AA)
- What It Means: The indicator that signals which page element is in focus is unobscured. “Sticky” elements on the page that don’t move as the user scrolls are the most common culprits that obscure key features.
- How To Succeed: People who can’t use a mouse need to see where the keyboard has focus. You’ll have succeeded if the item that has keyboard focus is at least partially visible as a user moves from one interactive element to another.
2.4.12 Focus Not Obscured (Enhanced) (AAA)
- What It Means: This also addresses the visibility of the keyboard focus, but it offers a path for organizations that want to go the extra mile.
- How To Succeed: You can satisfy 2.4.11 with partial visibility, but 2.4.12 requires complete visibility of the keyboard focus.
2.4.13 Focus Appearance (AAA)
- What It Means: This is an additional measurement criterion for how a website visually indicates what the keyboard focuses on. WCAG recommends a 3:1 contrast ratio for the colors for the focus state vs. the non-focus state and an outline or border around the entire element that is at least 2 CSS pixels thick. Background colors are acceptable as long as they still satisfy the contrast ratio.
- How To Succeed: WCAG 2.1 was ambiguous about what it meant for a focus indicator to be visible. This update clarifies what’s required with clear benchmarks for contrast and thickness/visibility.
Guideline 2.5: Input Modalities
An “input” is an action a user takes to elicit a response from your website — think clicking a button or dragging and dropping a feature. These standards govern the design of those inputs.
2.5.7 Dragging Movements (AA)
- What It Means: When an interface provides drag-and-drop functionality, there should be a simple pointer alternative that does not require drag-and-drop. This is more relevant for apps and web tools that will need to provide an alternative interface.
- How To Succeed: This standard serves users who can’t use a mouse or touch screen to drag items. You meet the standard by allowing a user to choose not to use the supplied drag-and-drop functionality unless dragging is considered “essential.”
2.5.8 Target Size (Minimum) (AA)
- What It Means: A minimum size and minimum space for an interactive element allows a user to choose one action without accidentally triggering a nearby action.
- How To Succeed: Some people with physical impairments may not be able to click buttons that are close together. For example, they might hit the “Cancel” button instead of “Submit,” forcing them to start the process over again. You can succeed with this guideline by ensuring the size of the target for pointer inputs is at least 24 by 24 CSS pixels, with some exceptions.
Guideline 3.2: Predictable
This guideline covers repeating features that may appear across your web pages, such as email sign-up forms or support widgets.
3.2.6 Consistent Help (A)
- What It Means: When a site or app has a help feature, it appears in the same location consistently.
- How To Succeed: People who need help can find it more easily if it’s in the same place. If a web page contains help mechanisms that repeat across pages, they should occur in the same order relative to other content on the page — unless the user initiates the change. Those help items can include human contact details, human contact mechanisms, self-help options, or a fully automated contact mechanism (i.e., a chat feature).
Guideline 3.3: Input Assistance
Many websites include elements that help users take certain actions. This could include directing a user to re-enter information or to make sure two fields match. Guideline 3.3 addresses this type of assistance, increasing WCAG’s support of those with cognitive disabilities. This puts the onus on developers to provide simple and secure methods for all users.
3.3.7 Redundant Entry (A)
- What It Means: Ask for information only once in the same session.
- How To Succeed: Some people with cognitive disabilities have difficulty remembering what they entered. If you’re asking the user to re-enter information they previously added, the field must either be auto-populated or the previous answer must be available for the user to select. The exception is if the user is re-entering information essential or required for security or the previous information is no longer valid.
3.3.8 Accessible Authentication (Minimum) (AA)
- What It Means: Don’t make people solve, recall, or transcribe something to log in.
- How To Succeed: Some people with cognitive disabilities can’t solve puzzles, memorize a username and password, or retype one-time passcodes. This guideline considers remembering a password or solving a puzzle (like a CAPTCHA) a cognitive function test. Websites that comply won’t require that step unless the step also provides an alternate authentication method, an assistive mechanism, a test with simple object recognition, or a test to identify non-text content the user provided to the website.
3.3.9 Accessible Authentication (Enhanced) (AAA)
- What It Means: This builds upon 3.3.8, offering developers a greater opportunity to include users with cognitive disabilities.
- How To Succeed: The success criteria for 3.3.9 are narrower than for 3.3.8. Websites meet the enhanced standard when a cognitive function test isn’t part of authentication unless the website also offers an alternative authentication method or a mechanism to assist the user with the test.
Walking the Walk of WCAG
A commitment to accessibility is two-fold. It requires understanding what the most recent guidelines are (the talk) and putting those guidelines into practice (the walk).
While it might seem like Level AAA accessibility is the way to go, the reality is that accessible websites are nuanced. Some level of accessibility is non-negotiable, but the ideal level for your site very much depends on your industry, your users, and how mature your website is — all factors we can better assess with an accessibility audit.
If you’re building a new website, embedding WCAG principles is smart. But if you’re WCAG 2.1 compliant and a refresh is a year or two off, WCAG 2.2 may be able to wait. Curious about where your website stands? Let’s talk about it.
The world of digital accessibility can be daunting. There are many regulations and ways in which a website can be accessible or inaccessible. Many of us don’t understand what a good or bad experience looks like, and we think we can’t possibly understand people who rely solely on assistive technology to use the web.
It doesn’t have to be daunting, though. And with anything, the key is to start small. To those who create websites or own/manage one, the first step to understanding accessibility is empathy. If more people used assistive technology, more people would understand the difference between a terrible experience and a great one. Don’t be scared of learning about accessibility tools, because you might already be more familiar with them than you realize.
Have you ever broken your dominant hand and been forced to use a keyboard instead of a mouse or trackpad? Have you tried to complete a payment form really quickly to snag concert tickets, and figured out that using the keyboard can be much faster?
Have you been in loud surroundings and tried to watch a video? How great are captions? Have you realized that captions are assistive technology? There are alternate modes of consuming content and using a digital product that are beneficial to a much wider audience than the audience it was created for.
With some instruction, we hope more people feel comfortable using a keyboard to navigate a website. We also hope that more of you are brave enough to try a screen reader as well, or at least watch our video to experience what that experience can be like.
Video Tutorial
Our video is 37 minutes and we provide a break-down of the different minute-marks below if you’d like to jump to a certain area. (All cookies must be accepted for the video to play. You may also view on YouTube directly.)
Table of Contents
- 00:00 — Using a Keyboard
- 02:00 — The tab key
- 02:20 — A “Skip to Content” link and why that is so useful
- 03:40 — “Focus ring” style
- 04:20 — An example of an inaccessible drop-down menu
- 05:40 — An example of an inaccessible link (no focus ring)
- 07:40 — Common article card patterns and how they work with a keyboard
- 10:45 — The Screen Reader Experience
- 11:10 — Invoking VoiceOver with Command F5
- 12:35 — Tabbing through interactive elements
- 12:54 — Skip to Content link
- 13:07 — Company logo
- 13:55 — Projects link
- 14:31 — Topics
- 15:55 — About Us link, inaccessible to keyboard users
- 16:16 — Reading of non-interactive elements with Control Option arrows
- 16:50 — Reading content, Headings, links
- 18:50 — Visually hidden heading but screen reader accessible
- 19:55 — Alt text image examples
- 20:06 — Kittens, no alt tag present
- 21:06 — Doggos, empty alt tag
- 23:00 — Squirrels, descriptive alt text
- 23:48 — Article content examples
- 23:53 — Article 1 example, too many links
- 25:37 — Article 2 example, too much content
- 26:32 — Article 3 example, hidden content
- 27:44 — Article 4 example, alternate pattern
- 30:02 — Voiceover’s Rotor Feature, control option U
- 30:15 — Headings menu
- 30:55 — Empty heading element
- 31:50 — Other Rotor menus
- 32:18 — Non-visited Links menu
- 33:01 — All Links menu
- 33:40 — “Click here” and “Read more” link text
- 35:09 — Landmarks menu
- 35:25 — Form Controls menu
- 36:06 VoiceOver off and wrap up
For those who want to learn a little more, below we collect a few keyboard command cheatsheets for navigating a webpage or using VoiceOver on a Mac. Links to additional resources for setting up and getting started with VoiceOver are also included.
More Resources
Keyboard User Cheatsheet
- Tab key — Navigate from link to link
- For sighted users who can still use a mouse: Getting started on a page might mean clicking into the top left corner to get the keyboard focus to be within the browser window and not on the desktop or in the browser (URL bar)
- In a Checkbox list in a form, the tab key will move from one element to another
- Return key (Enter) — “Presses” a link to open the destination or perform the one page action (for buttons)
- Spacebar
- When over an interactive element in a navigation, spacebar opens the element. Arrow keys may move up and down through the open list, or the tab key can be used. Spacebar again should toggle the element closed.
- In a Checkbox list in a form, the spacebar chooses the element currently in focus
- Escape key — Close most items that have been opened, like pop-up modal windows
- Arrows Up/Down — Generally, scrolls the page
- In a Radio Button group in a form, Tab will select the group of options while arrow keys will traverse the list
- With a Select list in a form, Tab makes the list active. Arrow keys traverses the list. Enter key selects the option in focus.
- Any letter key — With a Select list in a form, Tab makes the list active. When active and open, a letter key will jump to that letter in the list. Useful for long lists, like States or Countries.
VoiceOver Cheatsheet
These key commands reflect the default set-up for Mac OSX — I have not made any modifications. Of course, power users will modify these commands to fit their needs.
The default VoiceOver key command combination is ^Control ⌥Option. This combination is used to ensure key combinations do not conflict with other quick key commands through the OS and Apps.
Many key commands for navigating a webpage are the same as a Keyboard user. Return, Spacebar, and Arrow keys all work the same.
- ⌘Command F5 — Open and start Voiceover
- ^Control ⌥Option Arrow Right — Read next string of text
- ^Control ⌥Option Arrow Left — Read previous string of text
- ^Control ⌥Option Space — “Presses” a link or button
- For some elements, VoiceOver will announce that there are “Actions available.” Access the Actions menu with ^Control ⌥Option Space, and navigate the menu with the up and down arrow keys; press VO-Space to select a custom action.
- ^Control ⌥Option M — Access the Apple Menu (File, Edit, View, etc.). Escape Key returns to the web page content.
- ^Control ⌥Option H twice quickly — Commands Help menu
- While inside, arrow keys move up and down in lists. Left and Right arrows move from one list to another. Return key chooses an element from a list
- ^Control ⌥Option K — Keyboard Help. Similar to Command Help, but here, keys can be pressed without having any effect on the system (like a practice session). Escape key exits the Keyboard Help session
- ^Control ⌥Option U — Open the Rotor
- While inside, arrow keys move up and down in Rotor lists. Left and Right arrows move from one list to another. Return key chooses an element from a list, closes the Rotor, and moves focus to the selected element. Escape key exits the Rotor
- Traversing the page by Element Type:
- ^Control ⌥Option H — Find next heading
- ^Control ⌥Option L — Find next link (different from the Tab key as it will look for Links only, not buttons that perform on-page actions)
- ^Control ⌥Option J — Find next form control
- ^Control ⌥Option T — Find next table
- ^Control ⌥Option X — Find next list
- ^Control ⌥Option F — Find next frame
Additional Resources to Start Using VoiceOver
- Welcome to VoiceOver, Apple website
- Deep dive into using VoiceOver and customizing the system to work the way you prefer
Conclusion
With some practice, we hope you might find that using a keyboard to navigate can be your superpower. When filling out forms, for example, I use the keyboard almost exclusively to quickly move from one field to another and to find my state in a long drop-down list. Unless, of course, I run into another poorly coded form that is not accessible. Lucky for me, I can go back to using a mouse. But some do not have that option, and for them, our empathy should turn into empowerment and we shall demand better from our design and development practices.
For questions or to discuss how to make your next project more accessible, please contact us anytime.
More in Our Accessibility Series
Notable articles from the Accessibility category:
- Supporting Personal Safety: Best Practices with a Quick Exit Button
- Equity by Design with a new Inclusive Language Tool
- Redesign & Relaunch: Oomph’s Color Accessibility Tool for Designers gets a Redesign
- There is no Magic Wand: Plugins won’t fix accessibility
- Evolve your Best Practices: More Accessible HTML Forms
- Accessibility: Images, “Alt” tags, and the “Out Loud” Experience
- Accessibility is not only for Disabilities
There’s a new acronym on the block: MACH (pronounced “mock”) architecture.
But like X is to Twitter, MACH is more a rebrand than a reinvention. In fact, you’re probably already familiar with the M, A, C, and H and may even use them across your digital properties. While we’ve been helping our clients implement aspects of MACH architecture for years, organizations like the MACH Alliance have recently formed in an attempt to provide clearer definition around the approach, as well as to align their service offerings with the technologies at hand.
One thing we’ve learned at Oomph after years of working with these technologies? It isn’t an all-or-nothing proposition. There are many degrees of MACH adoption, and how far you go depends on your organization and its unique needs.
But first, you need to know what MACH architecture is, why it’s great (and when it’s not), and how to get started.
What Is MACH?
MACH is an approach to designing, building, and testing agile digital systems — particularly websites. It stands for microservices, APIs, cloud-native, and headless.
Like a composable business, MACH unites a few tried-and-true components into a single, seamless framework for building modern digital systems.
The components of MACH architecture are:
- Microservices: Many online features and functions can be separated into more specific tasks, or microservices. Modern web apps often rely on specialized vendors to offer individual services, like sending emails, authenticating users, or completing transactions, rather than a single provider to rule them all.
- APIs: Microservices interact with a website through APIs, or application programming interfaces. This allows developers to change the site’s architecture without impacting the applications that use APIs and easily offer those APIs to their customers.
- Cloud-Native: A cloud-based environment hosts websites and applications via the Internet, ensuring scalability and performance. Modern cloud technology like Kubernetes, containers, and virtual machines keep applications consistent while meeting the demands of your users.
- Headless: Modern Javascript frameworks like Next.js and Gatsby empower intuitive front ends that can be coupled with a variety of back-end content management systems, like Drupal and WordPress. This gives administrators the authoring power they want without impacting end users’ experience.
Are You Already MACHing?

Even if the term MACH is new to you, chances are good that you’re already doing some version of it. Here are some telltale signs:
- You have one vendor for single sign-on (SSO), one vendor to capture payment information, another to handle email payment confirmations, and so on.
- You use APIs to integrate with tech solutions like Hubspot, Salesforce, PayPal, and more.
- Your website — or any website feature or application — is deployed within a cloud environment.
- Your website’s front end is managed by a different vendor than its back end.
If you’re doing any of the above, you’re MACHing. But the magic of MACH is in bringing them all together, and there are plenty of reasons why companies are taking the leap.
5 Benefits of MACH Architecture
If you make the transition to MACH, you can expect:
- Choice: Organizations that use MACH don’t have to settle for one provider that’s “good enough” for the countless services websites need. Instead, they can choose the best vendor for the job. For example, when Oomph worked with One Percent for America to build a platform offering low-interest loans to immigrants pursuing citizenship, that meant leveraging the Salesforce CRM for loan approvals, while choosing “Click and Pledge” for donations and credit card transactions.
- Flexibility: MACH architecture’s modular nature allows you to select and integrate individual components more easily and seamlessly update or replace those components. Our client Leica, for example, was able to update its order fulfillment application with minimal impact to the rest of its Drupal site.
- Performance: Headless applications often run faster and are easier to test, so you can deploy knowing you’ve created an optimal user experience. For example, we used a decoupled architecture for our client Wingspans to create a stable, flexible, and scalable site with lightning-fast performance for its audience of young career-seekers.
- Security: Breaches are generally limited to individual features or components, keeping your entire system more secure.
- Future-Proofing: A MACH system scales easily because each service is individually configured, making it easier to keep up with technologies and trends and avoid becoming out-of-date.
5 Drawbacks of MACH Architecture
As beneficial as MACH architecture can be, making the switch isn’t always smooth sailing. Before deciding to adopt MACH, consider these potential pitfalls.
- Complexity: With MACH architecture, you’ll have more vendors — sometimes a lot more — than if you run everything on one enterprise system. That’s more relationships to manage and more training needed for your employees, which can complicate development, testing, deployment, and overall system understanding.
- Challenges With Data Parity: Following data and transactions across multiple microservices can be tricky. You may encounter synchronization issues as you get your system dialed in, which can frustrate your customers and the team maintaining your website.
- Security: You read that right — security is a potential pro and a con with MACH, depending on your risk tolerance. While your whole site is less likely to go down with MACH, working with more vendors leaves you more vulnerable to breaches for specific services.
- Technological Mishaps: As you explore new solutions for specific services, you’ll often start to use newer and less proven technologies. While some solutions will be a home run, you may also have a few misses.
- Complicated Pricing: Instead of paying one price tag for an enterprise system, MACH means buying multiple subscriptions that can fluctuate more in price. This, coupled with the increased overhead of operating a MACH-based website, can burden your budget.
Is MACH Architecture Right for You?
In our experience, most brands could benefit from at least a little bit of MACH. Some of our clients are taking a MACH-lite approach with a few services or apps, while others have adopted a more comprehensive MACH architecture.
Whether MACH is the right move for you depends on your:
- Platform Size and Complexity: Smaller brands with tight budgets and simple websites may not need a full-on MACH approach. But if you’re managing content across multiple sites and apps, managing a high volume of communications and transactions, and need to iterate quickly to keep up with rapid growth, MACH is often the way to go.
- Level of Security: If you’re in a highly regulated industry and need things locked down, you may be better off with a single enterprise system than a multi-vendor MACH solution.
- ROI Needs: If it’s time to replace your system anyway, or you’re struggling with internal costs and the diminishing value of your current setup, it may be time to consider MACH.
- Organizational Structure: If different teams are responsible for distinct business functions, MACH may be a good fit.
How To Implement MACH Architecture
If any of the above scenarios apply to your organization, you’re probably anxious to give MACH a go. But a solid MACH architecture doesn’t happen overnight. We recommend starting with a technology audit: a systematic, data-driven review of your current system and its limitations.
We recently partnered with career platform Wingspans to modernize its website. Below is an example of the audit and the output: a seamless and responsive MACH architecture.
The Audit
- Surveys/Questionnaires: We started with some simple questions about Wingspan’s website, including what was working, what wasn’t, and the team’s reasons for updating. They shared that they wanted to offer their users a more modern experience.
- Stakeholder Interviews: We used insights from the surveys to spark more in-depth discussions with team members close to the website. Through conversation, we uncovered that website performance and speed were their users’ primary pain points.
- Systems Access and Audit: Then, we took a peek under the hood. Wingspans had already shared its poor experiences with previous vendors and applications, so we wanted to uncover simpler ways to improve site speed and performance.
- Organizational Structure: Understanding how the organization functions helps design a system to meet those needs. The Wingspans team was excited about modern technology and relatively savvy, but they also needed a system that could accommodate thousands of authenticated community members.
- Marketing Plan Review: We also wanted to understand how Wingspans would talk about their website. They sought an “app-like” experience with super-fast search, which gave us insight into how their MACH system needed to function.
- Roadmap: Wingspans had a rapid go-to-market timeline. We simplified our typical roadmap to meet that goal, knowing that MACH architecture would be easy to update down the road.
- Delivery: We recommended Wingspans deploy as a headless site (a site we later developed for them), with documentation we could hand off to their design partner.
The Output
We later deployed Wingspans.com as a headless site using the following components of MACH architecture:
- Microservices: Wingspans leverages microservices like Algolia Search for site search, Amazon AWS for email sends and static site hosting, and Stripe for managing transactions.
- APIs: Wingspans.com communicates with the above microservices through simple APIs.
- Cloud-Native: The new website uses cloud-computing services like Google Firebase, which supports user authentication and data storage.
- Headless: Gatsby powers the front-end design, while Cosmic JS is the back-end content management system (CMS).
Let’s Talk MACH
As MACH evolves, the conversation around it will, too. Wondering which components may revolutionize your site and which to skip (for now)? Get in touch to set up your own technology audit.
Feel like you’re seeing a lot more website pop-up banners these days asking about your cookie preferences? Those cookie banners are here to stay, and they’re a vital part of compliance for websites of all sizes.
As global standards for consumer privacy and data protection continue to climb, businesses are burning more time and resources to keep up. One VentureBeat article pegged the cost for a business of maintaining data privacy compliance at an eye-popping $31 million — and the costs of non-compliance can be even higher. Failing to stay on top of this complex patchwork of regulations can trigger real consequences, from steep fines and penalties to the indirect costs of reputational harm and lost business.
Cookie consent is one part of a holistic data privacy strategy — and an increasingly important one. Global privacy laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and Brazil’s General Data Protection Law (LGPD), require companies to inform visitors about the data collected on their website via cookies and provide them with granular choices about what they’re willing to share. Cookie consent management solutions help users manage cookie preferences when they enter your site, presenting a banner that informs users about how cookies are used and letting them decide which information (if any) they want cookies to collect.
Cookie consent management solutions are rapidly evolving to keep up with changing data privacy standards. CookiePro is a solution from OneTrust designed specifically for small to medium businesses, offering a more automated way to ensure website and mobile applications stay compliant with cookie consent and global privacy regulations. At Oomph, we’ve helped several clients integrate CookiePro into their sites in recent months and think it’s on track to become an industry standard for cookie consent management.
For organizations that are already juggling multiple site integrations, does it make sense to add another? To answer that, let’s take a look at why cookie consent matters, how a tool like CookiePro can help, and if it’s right for you.
Why Do I Need a Cookie Consent Solution?
To comply with privacy laws and provide a transparent experience that builds trust, many website owners are rethinking how they manage compliance. Adding a cookie consent tool to your website can improve the experience for you and your users.
Ensure Compliance
Not taking data privacy seriously can cost you. In December 2022, Meta (the parent company of Facebook) agreed to pay $725 million to settle several class-action lawsuits that found Facebook had let third-parties access users’ private data and their friends’ data without user permission. Oracle has been sued for collecting 4.5 billion personal records from consumers who have specifically opted out of sharing, and Starbucks is potentially facing a lawsuit for continuing to “track customers ‘after they’ve declined all but required cookies.’”
While big-name companies get most of the bad press around data privacy, you don’t have to be a global enterprise to face similar consequences. In 2022, the total value of settlements for class-action lawsuits set a new record at $63 billion — and data breach and privacy class action settlements were among the top 10 settlement categories. Instead of risking a costly settlement, a much less expensive approach is to invest in a solution to help manage the work of compliance.
Build Trust
Beyond protecting your organization from legal action, demonstrating that you care about compliance helps your business build trust and long-term relationships with users. Data privacy is becoming more important to consumers of all ages, with 74% of people ranking data privacy as one of their top values.
A cookie consent solution lets users know that they’re in charge of their own data. It clearly discloses which information your business collects and uses, putting the power in their hands to control the data they share. If users want to change what they’re comfortable sharing later, they can easily update their settings. That level of transparency helps set the tone for your customer interactions, turning users into loyal brand advocates.
Optimize Efficiency
If your website serves users in multiple states or countries, keeping up with the patchwork of state, federal, and international laws is virtually impossible without software. Eleven states have unique data privacy laws in place right now, and 16 states introduced privacy bills during the 2022 to 2023 legislative cycle.
Factor in international regulations like GDPR, and it would take more hours than there are in a day to curate the individual preferences of your customer base. Plus, which of your team members is watching in case any regulations change? The most efficient approach is to use an automated cookie solution to curate consent requirements based on the user’s location and more.
What Is CookiePro?
Developed by OneTrust, which offers more robust data privacy solutions for enterprises, CookiePro started as a product in the OneTrust platform. After recognizing the need among small and medium businesses for a turnkey consent tool, OneTrust spun off CookiePro as a standalone solution.
CookiePro offers plans starting at around $40 per month, making it a budget-friendly alternative to enterprise solutions like OneTrust (or the cost of a lawsuit settlement). CookiePro comes with core compliance features like user-level consent management, acceptance customization, data mapping and recordkeeping, support for over 250 user languages, and additional security features.
After helping several of our clients implement CookiePro, there are a few key features that stand out for us:
- Easy installation: It just takes a few minutes to add a snippet of code to your website to enable CookiePro. It’s compatible with Drupal, WordPress, and other major site platforms.
- Automated cookie blocking: CookiePro’s auto-blocking tool scans your website to identify third-party tracking technologies, categorizes the cookies, and automatically blocks all cookies until users have given consent.
- Robust customizations: You can tailor your CookiePro banner to match your branding by customizing colors, content, and consent language. CookiePro also allows you to customize the user experience by choosing your consent approach and giving users granular control over their cookie settings.
- Upgrade path: Whether you have a small site or one with hundreds of thousands of visitors, CookiePro can support growing business needs. If you find that you need more support or functionality, you can upgrade to OneTrust’s Trust Intelligence Platform to unify all your data privacy management activities.
- Tag management system integrations: You can integrate tag management systems with your cookie consent solution if you use analytics and other platform tags on your website. CookiePro has integrations with many major tag management systems, including Google Tag Manager and Tealium, so you don’t have to change your current setup.
Beyond CookiePro, there are a growing number of other cookie consent solutions on the market, such as Termly and Cookiebot by Usercentrics. The right choice for you will depend on your existing tech stack, budget, and goals — the most important step is to put something in place to protect yourself and your users.
Where Should I Start?
Taking a proactive approach is key to ensuring data privacy for your users and avoiding costly consequences. Educate yourself on the different regulations and requirements, figure out the gaps in your compliance approach, and invest in tools that can help reduce risk and manual effort for your team.
Feeling overwhelmed or need a fresh perspective? Oomph’s accessibility and compliance audit is a great place to start. We can help you go beyond cookie consent to meet Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), Americans With Disabilities Act (ADA), and other regulatory standards, helping you mitigate risk and deliver on user expectations. Reach out to us to schedule your site audit.
What’s been holding you back from migrating your website off of Drupal 7?
Maybe your brand is juggling other digital projects that have pushed your migration to the back burner. Maybe the platform has been working well enough that migration isn’t really on the radar. Or maybe (no shame here) you’ve been overwhelmed by such a massive undertaking and you’re feeling a little like Michael Scott:

“I don’t wanna work. I just want to bang on this mug all day.”
We get it. Whether you’re migrating to a new version of Drupal or a different platform, it’s a time-consuming process — which means now is definitely the time to get started.
While the Drupal Security Team recently announced it would extend security coverage for Drupal 7 from November 2023 to January 2025, those extra 14 months are ideally the time to plan and execute a thoughtful migration. Giving yourself ample time to plan for life after Drupal 7 is something Oomph has been recommending for a while now, and we’re here to help you through it.
3 Reasons To Start Your Drupal 7 Migration Now
1. Because Migration Takes Time
Migrating your site isn’t as simple as flipping a switch — and the more complex your site is, the more time it can take. Imagine two boats changing course in the water: It takes a massive container ship longer to turn than a small fishing boat. If your site is highly complex or has a lot of pages, it could easily take a year to fully migrate (not including the time it takes to select a partner to manage the process and kick off the work).
Even if your site isn’t so robust, you’ll do yourself a favor by building in a time buffer. Otherwise, you could risk facing a security gap if you run into complications that slow the process down. Some of the major factors that can impact timeline include:
- Developing a new site theme. The switch from the PHP Template Engine in Drupal 7 to Twig in Drupal 8 and above means you’ll need to rewrite your custom theme if you’re planning to upgrade to Drupal 10 — even if you’re not planning to redesign your site.
- Navigating custom code. If your current site relies on custom code, those modules will need special attention during the migration process.
- Migrating community-contributed modules. One of the best things about Drupal is the fact that it’s open-source, which means community members are constantly contributing new modules and features that anyone can use. While many Drupal 7 modules have a simple migration path to Drupal 10, not all do. Certain modules, including Organic Groups, Field Collections, and Panels, will need to be reviewed and migrated manually. Even if a module has a set migration path, it can be quicker to migrate them by hand (Webforms and Views are two good examples).
- Making other upgrades. You know the old saying, “Never let a good migration go to waste?” (OK, we made that up.) Still, a migration is a smart time to tackle other changes to your site, from updating your information architecture to modernizing your design. If you’re planning on a more holistic site update, there’s even more reason to start now to make sure your project is wrapped before the end of 2024.
2. Your Site Performance Is Less Than Ideal
Yes, Drupal 7 sites technically have security coverage until 2025. But if you’re still on Drupal 7, you’re missing out on the best that Drupal currently has to offer.
First, Drupal 7 is not fully compatible with PHP 8, a new and improved version of PHP that many websites are built on today. While Drupal 7’s core supports PHP 8, some contributed modules or themes on your site might not, which could create hiccups in your site performance.
In addition, the Drupal community is constantly putting out new features that aren’t available on Drupal 7. Some of the most exciting ones include:
- Layout builder, a visual design tool that makes it easier for content editors to build web pages and gives designers more room to flex their creative muscles.
- Workspaces, an experimental feature that allows users to stage content or preview a full site by using multiple workspaces on a single site.
- Better accessibility and responsive design to create genuinely useful experiences for all site users.
- API-first architecture and decoupled options to make it easier to integrate your site with any other tools or functionality you need.
- Twig, a templating language from Symfony that lets you write concise, readable templates that are more friendly to web designers.
- SaaS offerings like Acquia’s Site Studio to build beautiful pages more easily.
Sticking with Drupal 7 means not only missing out on this new functionality, but also on support from the Drupal community. Interest and activity from web devs on Drupal 7 continues to wane, which means your team may find it harder to get help from others to deal with bugs or other issues. You’re also likely to see fewer new features that are compatible with the older version – so while other sites can keep up with the evolving digital landscape, a Drupal 7 site is increasingly stuck in the past.
3. To Save Your Team’s Sanity
Odds are good that if your site is still running on Drupal 7, your team is already having trouble trying to make it work for your needs. Starting your migration now is key to getting your site running as smoothly as soon as possible — and sparing your team from unnecessary misery.
Consider these pain points and how your team can address them in your migration:
- Is your team frustrated with aspects of Drupal 7 that limit your site’s functionality?
- Is technical debt making your site maintenance more complicated, expensive, or both? Could it be affecting your hosting or vendor costs?
- Is your team struggling to find support or third-party integrations that work with the platform?
- Are they holding off on major new initiatives because the site can’t support them?
Options for Life After Drupal 7
Now that Drupal 7 is officially winding down, what’s next for your website? Deciding whether to go Drupal-to-Drupal, Drupal to another CMS, or a different route entirely depends on your technical needs and resources.
Drupal 10
If Drupal 7 has served your team well in the past, then Drupal 10 is the logical choice. The newest version of Drupal is ideal for more complex sites with extensive content modeling, varying user roles, and workflow requirements. To make things easier, you can leapfrog over Drupal 8 and 9 and migrate your Drupal 7 site directly to the latest and greatest version.
Many of our clients at Oomph are going this route, since Drupal 10 offers both a range of new features and familiarity for Drupal-versed teams to cut down on the post-migration learning curve.
WordPress or Another CMS
Not sure if Drupal 10 is the best fit? If your site is on the small side or if you don’t require lots of functionality, then Drupal may be more than you really require.
In that case, moving off of Drupal altogether might be in your best interests, helping you streamline your ongoing development needs and reduce maintenance and hosting costs. Here are a few alternatives for Drupal 7 users looking for a less robust platform without sacrificing a great web presence:
- WordPress
- Squarespace
- Wix
- Consider a headless CMS, supported by a decoupled framework such as Gatsby or Next.js.
An Internal Stopgap
Depending on your organization, now might not be a good time to migrate or rebuild your site. This is especially true if you’re already invested in an ongoing site redesign or rebuild. If you’re still trying to figure out your digital future, consider temporary measures you can take to stay protected once Drupal 7’s security coverage ends.
One possibility to consider is rolling up your site under another digital property in your organization. Even if it’s only an interim solution, it can help you buy time to make the best long-term plan for your website. Another option would be to develop a smaller static website with a refreshed design that would eventually be replaced with the upgraded CMS.
Tips for a Successful Migration
As your site’s technical foundation, Drupal delivers plenty of horsepower. However, the digital home you build on that foundation is what really counts. It’s crucially important to make sure all the pieces of your site work together as one — and a migration is a perfect opportunity to assess and optimize.
Over time, websites tend to accumulate “cruft” — the digital equivalent of dust and cobwebs. Cruft can take many forms: outdated, unnecessary, or poorly written code; deprecated site features; or obsolete or outdated content, files, and data. Whatever cruft exists on your site, migration is a chance to do some digital spring cleaning that can improve site performance and reduce maintenance time.
Beyond digital hygiene, evaluating each element of your site strategically can help you get the greatest business value from your migration.
- Information architecture: How easy is it to navigate around your site? Do your sitemap and information architecture still reflect your offerings and user needs accurately?
- Content: Does your site’s content still engage your audience and support business goals? Think about the impact of any changes to your information architecture: Would they require you to add, change, or remove content?
- Design: Will your existing site design work with the CMS you’ve chosen? Does it need updates to meet current standards for UX, accessibility, and responsiveness?
- Integrations: Should you add or remove any APIs or integrations? Keep in mind that many features not available in Drupal 7 are now built into the core of Drupal 10 or are available as contributed modules, so you may be able to optimize some of your site’s key features.
No matter what you plan to tackle alongside your migration, it’s a big project. An experienced guide can make all the difference. Our team of die-hard Drupal enthusiasts has led many Drupal-to-Drupal and replatforming projects for clients, including complex e-commerce and intranet sites. For us, a successful migration is one that’s grounded in strategy, follows technical best practices, and — most importantly — can support and evolve with your brand over time.
Need a hand deciding which route to take for your Drupal 7 migration? We’d love to talk.
Finding yourself bogged down with digital analytics? Spending hours just collecting and organizing information from your websites and apps? Looker Studio could be the answer to all your problems (well, maybe not all of them, but at least where data analytics are concerned).
This business intelligence tool from Google is designed to solve one of the biggest headaches out there for marketers: turning mountains of website data into actionable insights. Anyone who’s ever gone down the proverbial rabbit hole scouring Google Analytics for the right metrics or manually inputting numbers from a spreadsheet into their business intelligence platform knows that organizing this data is no small task. With Looker Studio, you can consolidate and simplify complicated data, freeing up more time for actual analysis.
With so many customizable features and templates, it does take time to set up a Looker Studio report that works for you. Since Google’s recent switch from Universal Analytics to Google Analytics 4, you might also find that certain Looker Studio reports aren’t working the way they used to.
Not to worry: Our Oomph engineers help clients configure and analyze data with Looker Studio every day, and we’ve learned a few tips along the way. Here’s what to know to make Looker Studio work for your business.
The benefits of using Looker Studio for data visualization and analysis
Formerly known as Google Data Studio, Looker Studio pulls, organizes, and visualizes data in one unified reporting experience. For marketers who rely heavily on data to make informed decisions, Looker Studio can save precious time and energy, which you can then invest in analyzing and interpreting data.
Key benefits of using Looker Studio include:
- Connecting data from multiple sources: The platform can unify data from a mind-boggling 800+ sources and 600+ data connectors, which means you can upload and integrate multiple data sets into one comprehensive report. This not only saves time, but also provides more accurate insights into business performance for organizations with complex digital environments.
- User-friendly insights: Looker Studio’s visual dashboards are easy to interpret, customize, and share – even with executives who might not be as digitally fluent as you. You can choose from a variety of drag-and-drop data visualization options, such as charts, graphs, and tables, or use Looker Studio’s pre-designed visualizations.
- Powerful customization: Want to be informed the minute your form conversion rate changes? With Looker Studio, you can set up alerts to notify you of significant changes in your data, enabling you to adjust your marketing strategy and optimize ROI in real time. You can also generate reports to track your progress and share them with your clients or team members.
How Oomph uses Looker Studio
As a digital-first company in the business of helping other digital-first companies, we’re big fans of Looker Studio. We think the platform is a great way to share trends on your websites and apps in an easy-to-digest way, making monthly or quarterly reporting much more efficient.
Whether you’re looking for basic insights or need sophisticated analysis, Looker Studio’s visualization capabilities can support smarter, more informed digital decision-making. Here’s a peek at some of the metrics we monitor for our own business, including:
- Number of users
- New users versus returning users
- Average time spent on site and on page
- Top pages viewed
- Traffic sources
- Traffic by device
- Event tracking and conversion rates
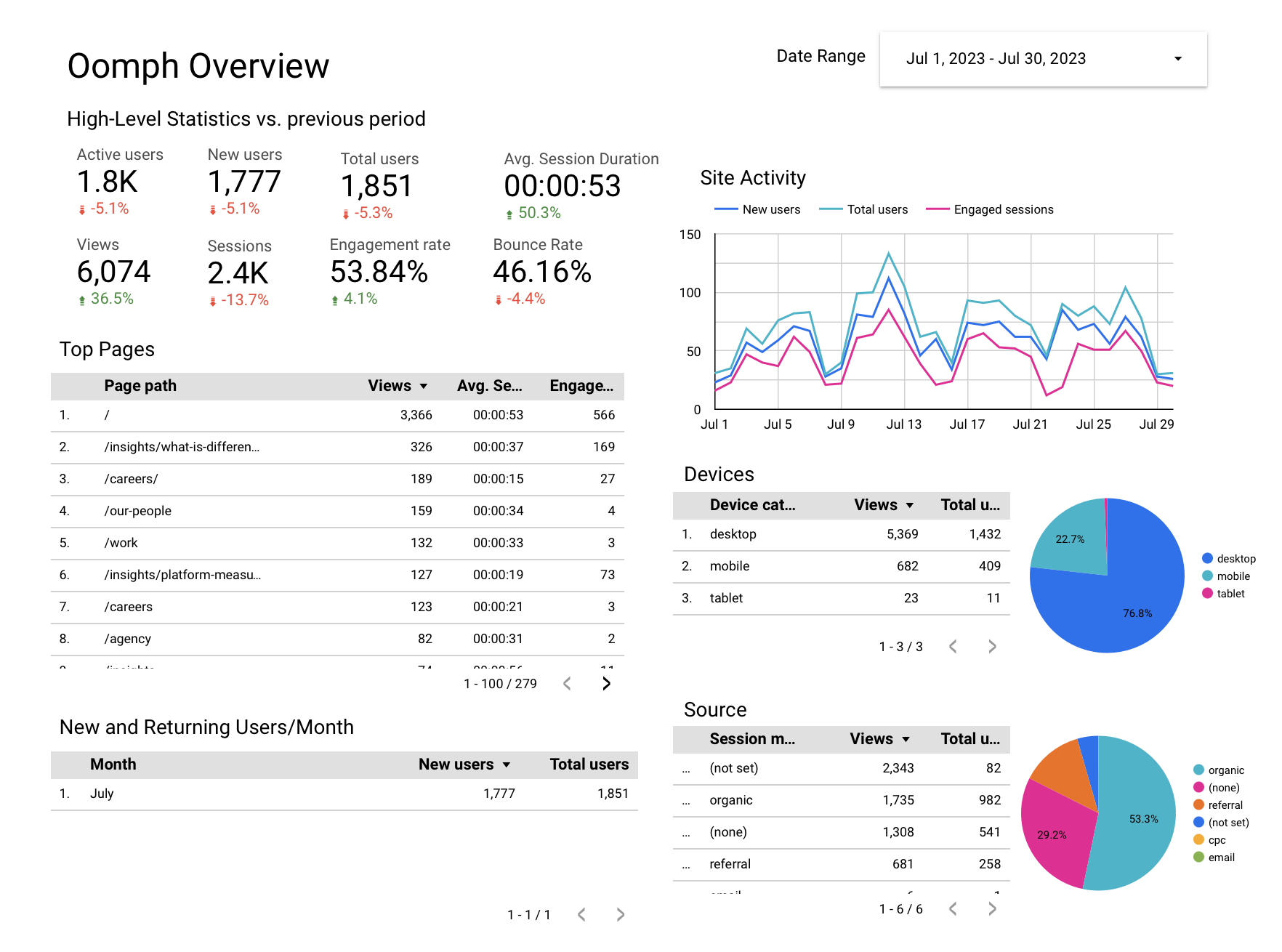
We also use the platform to drill deeper, comparing trends over time, identifying seasonal fluctuations and assessing the performance of specific campaigns. We leverage features like dashboards and filters in Looker Studio to give our clients an interactive view of their data.
How Looker Studio Works With GA4
Google Analytics, now known as GA4, is one of the primary tools we connect to Looker Studio. GA4 is the latest version of Google’s popular analytics platform and offers new features and functionality compared with its predecessor, Universal Analytics (UA), including new data visualization capabilities.
As many companies migrate over to GA4, they may be wondering if reporting will be similar between GA4 and Looker Studio – and if you need both.
While GA4 reports may challenge Looker Studio’s capabilities, Looker Studio provides a variety of features that go beyond what GA4 can do on its own. While GA4 dashboards and reports just include GA4 data, Looker Studio can import data from other sources as well. This means you can use Looker Studio to track trends in your site’s performance, regardless of the data source.
Looker Studio also has a unique feature called “LookML,” which allows users to create custom data models and transformations. This means you can tailor your data to your specific needs, rather than being limited by GA4’s built-in reporting. Finally, Looker Studio’s robust sharing and collaboration features allow teams to share data and insights easily and efficiently.
If your company set up Looker Studio before switching to GA4, you may notice a few metrics are now out of sync. Here are a few adjustments to get everything working correctly:
- Average time on page: This was previously a standard feature in UA that’s no longer available in GA4. To configure, you’ll need to track the “user engagement” metric divided by “number of sessions.”
- Bounce rate: Tracking bounce rate with GA4 now takes an additional step as well. To configure, subtract the “engagement rate” metric from 1 to arrive at your bounce rate.
- Events: Simply update your Looker Studio connection settings to use the new GA4 event schema and ensure that you’re using the correct event names and parameters in your LookML code.
How To Set Up a Looker Studio Report
- Choose a template for your dashboard or create one from scratch. If you’re not sure, you can browse through templates to get an idea of what Looker can do.
- Connect your data source. Looker supports a long list of sources, including Google, MySQL, AWS Redshift, and more. Don’t worry if your data isn’t in Google – Looker will likely be able to connect to it regardless.
- Choose your metrics. These are the specific data points you want to track and analyze in your report. You can customize your metrics to fit your specific needs.
- Build your dashboard. You can add charts, tables, and other visualizations to help you understand your data. Looker makes it easy to drag and drop these elements into place.
- Share it with others. You can either create a share link so that others can access the dashboard directly or you can set up automatic updates to be sent on a regular basis. This makes it easy for others to stay up-to-date on changes and progress.
A Powerful Path To Data Insights
The digital landscape is growing more fragmented and complex by the day, but tools like Looker Studio make it infinitely easier to find your path forward. Taking the time to configure and customize the platform can deliver major ROI by helping you understand user needs, pinpoint website strengths and challenges, and craft the right digital strategy.
Crunched for time or not sure where to start? Oomph can help take the hassle out of data analysis by setting up and monitoring your Looker Studio dashboards. Get in touch to chat about your needs.